Hearing Loss
Hearing loss impacts one in six adults. While hearing loss symptoms generally impact those of more advanced age, research has shown that hearing loss is also affecting more young people than ever before. This can often be due to factors such as noise-induced hearing loss and hearing loss due to an ear infection, with hearing loss in children on the rise.
If you’re facing hearing problems and would like some advice on the most appropriate hearing loss treatment for you, get in touch with our expert team today.

The impacts of hearing loss
Hearing loss can negatively impact various aspects of everyday life; communication that once came naturally can become increasingly difficult and tiring.
As active communication requires intense concentration, it can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness due to the difficulties experienced when talking in groups of people.
Causes of hearing loss
There are many different causes for hearing loss, with hearing loss symptoms differing in levels of severity. Some causes for hearing loss can lead to individuals experiencing hearing loss in only one ear while they can hear perfectly out of the other.
Here are a few examples of the main causes of hearing loss:
Hearing loss causes: The Affected Areas
Hearing loss causes can stem from several issues in each area of the ear as follows. It is important that any signs and symptoms of hearing loss are dealt with as soon as possible.
Hearing loss caused by an outer or middle ear defect is called conductive hearing loss whereas damage to the inner ear is called sensorineural hearing loss. If both types occur together, the condition is called mixed hearing loss.
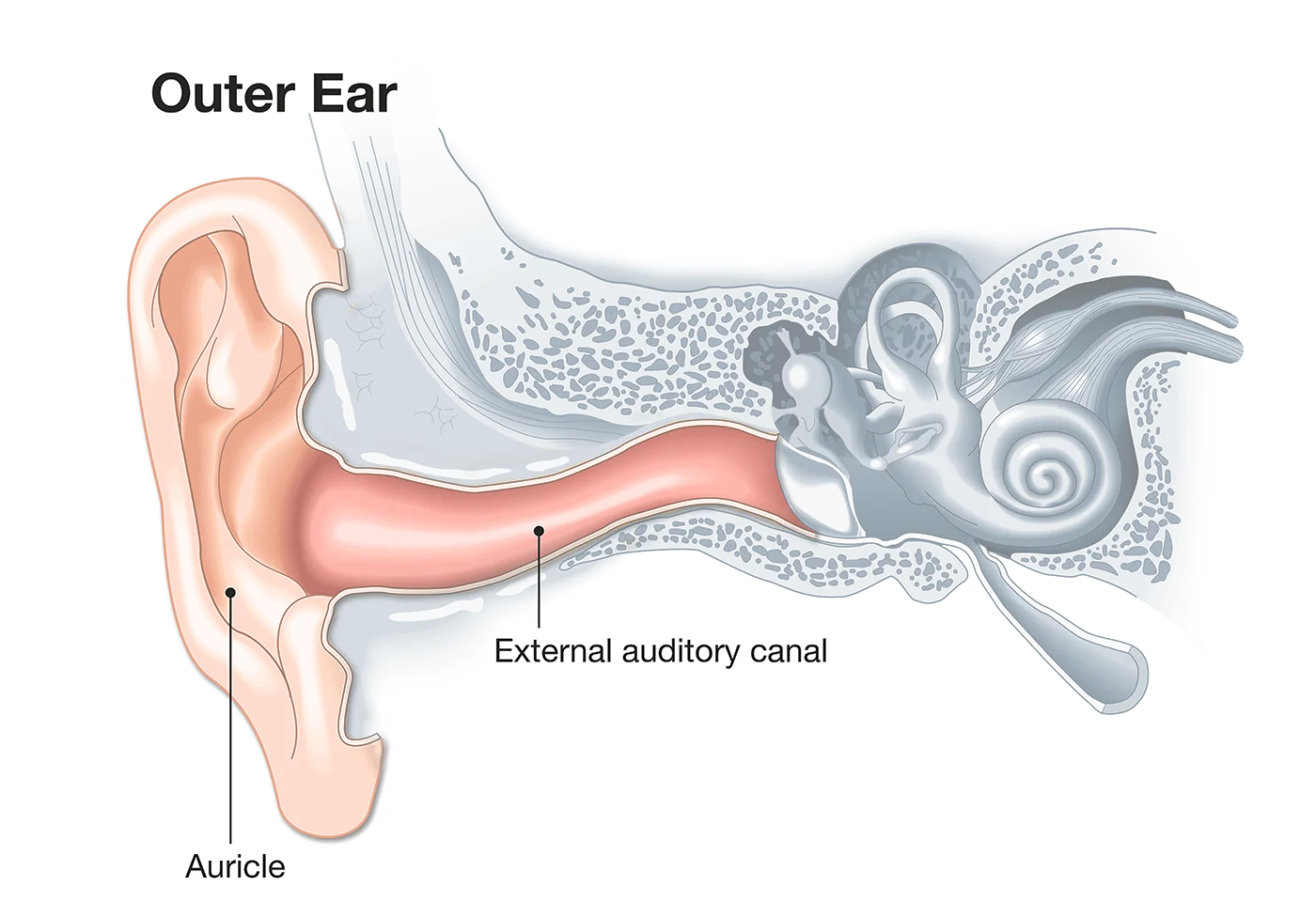
Hearing Loss Causes: The Outer Ear
Hearing loss causes can result from issues within the outer ear. Typical problems with the outer ear include ear wax blockages and infections of the auditory canal.
Usually, these problems can be addressed by ear wax removal or visiting your GP for infections. It is important to act quickly to avoid hearing damage.
Hearing Loss Causes: The Middle Ear
Inflammation, fluid behind the eardrum, perforations of the eardrum and otosclerosis (a stiffening of the bones in the middle ear) are the most common problems to interfere with middle ear function causing hearing loss.
Most middle ear problems can be addressed effectively with medication or surgery. If this is not possible, permanent hearing loss can be compensated with a hearing aid in most cases.

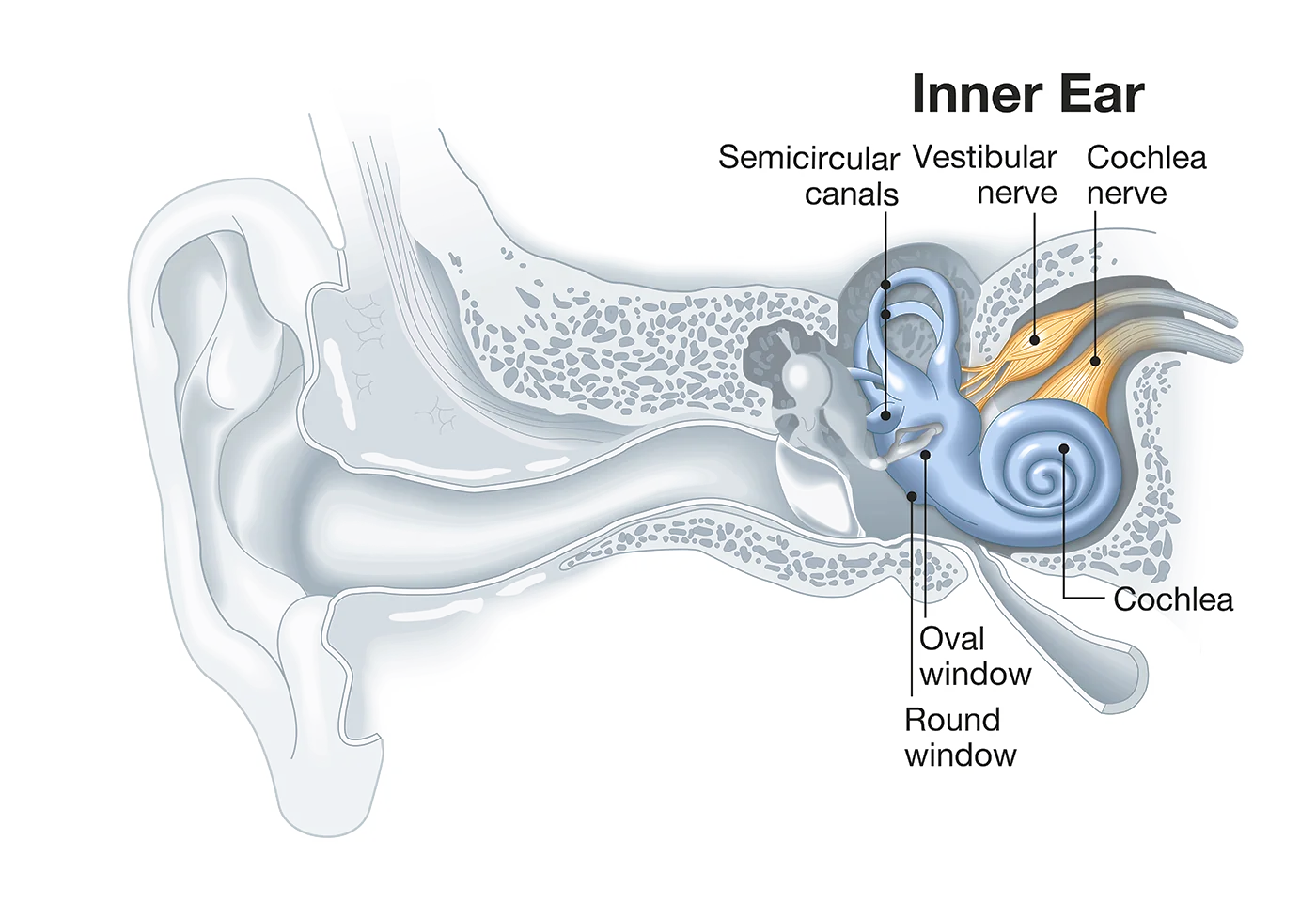
Hearing Loss Causes: The inner Ear
Most hearing loss causes stem from the symptoms in the inner ear. The most common cause is the natural ageing process. But loud noise, taking certain medication, or skull fractures can also have a negative influence on a person’s hearing ability. These influences damage the fine hair cells and affect the transmission of signals to the auditory nerves.
Usually, inner ear hearing loss cannot be addressed medically. However, this type of hearing loss can be corrected with hearing aids in most cases.
Hearing Loss Levels
Audiograms will show the categories of hearing loss, so that you can better understand your level of hearing. During the hearing assessment, our audiologists will perform audiometry alongside an examination of your ears. The audiogram is a chart displaying the results of audiometry, with frequency (measured in hertz) running along the x axis and loudness (measured in decibels) running along the y axis. Each ear is measured separately, and the results are saved to allow us to monitor your hearing moving forward.
The table adjacent shows the hearing loss categories and how it might equate to your day-to-day experiences with your hearing.
If your hearing lies outside of the normal range, you may benefit from hearing aids that will make social interactions and listening to music easier. We provide demonstration appointments after the hearing assessment, to enable you to find the right solution for your hearing.
| Hearing Loss Descriptor | Average Hearing Threshold Levels (dB HL) | Expectations |
| Normal hearing | < 20 | Little to no hearing difficulties |
| Mild | 21 – 40 | Begin to struggle with background noise and quiet speech |
| Moderate | 41 – 70 | Struggle with background noise, quiet speech, and louder TV/radio volumes may be required |
| Severe | 71 – 90 | Struggle with regular conversation, background noise, louder TV/radio volumes are required |
| Profound | > 90 | Extremely difficult to hear most sounds |
Understanding Your Hearing Loss Chart
At Harley Street Hearing, we can help you understand the results of your hearing test and provide expert advice and solutions. If you’d like a hearing test please book a consultation today by contacting us, and discover more about the services we offer including hearing protection and tinnitus therapy.

Begin your journey to great hearing