What happens at a hearing test?
Are you looking to book a hearing test and are wondering what happens? It’s natural to be curious, and sometimes worried, about how the tests are performed and what exactly is evaluated.
In this article, we’ve outlined how a hearing test is carried out, how to prepare for a hearing test and what to expect after your test is complete.
What is a hearing test?
A hearing test is a non-invasive procedure that is used to evaluate how the ear is functioning and determine if there are any hearing-related issues or impairments. Hearing tests are carried out by an audiologist who specialises in the diagnosis and management of hearing loss.
Hearing tests evaluate your ability to hear different frequencies or pitches of sound, your ability to understand speech, and the function of the middle ear and inner ear hair cells.
Our standard hearing test takes approximately 30 minutes from start to finish, including an explanation of your test results. However, if you’re experiencing signs of hearing loss, we suggest an in-depth hearing assessment. Our 90 minute hearing assessments include a personalised lifestyle assessment and independent advice on the most appropriate hearing technology to meet your individual needs.
Harley Street Hearing has over 25 years of clinical experience helping others improve their hearing ability and quality of life. We are independent audiologists and are registered with the Health and Care Professions Council which means you can book with us directly without the need for a referral from your GP or ENT consultant.

How to prepare for a hearing test
To get the most out of your hearing test and ensure your results are as accurate as possible, there are a number of simple steps you can take prior to the appointment to prepare your ears.
Clean your ears
Before a hearing test, we always recommend that your ears are clean and free of any earwax or debris that could interfere with the accuracy of the test. If you have any concerns about the cleanliness of your ears, you can book an earwax removal appointment with one of our highly trained clinical audiologists prior to your hearing test.
Check your medications
We also ask that you make a note of which medications you’re taking prior to your appointment. Some medications and conditions can affect your hearing capacity and your clinical audiologist will need to be aware of which medications you take or conditions you have.
Avoid loud noises
Where possible, it is best to avoid loud noises prior to your appointment. Loud noises that result in ringing of the ear can make it harder for you to accurately perform in our hearing tests which can change the outcome of your evaluation.
Rearrange if you’re unwell
It’s never a good idea to attend a hearing test appointment when you’re unwell. This is because illnesses such as colds and sinus infections can affect the way we hear. If you’re feeling under the weather, it’s better to arrange your appointment for when you’re feeling better.
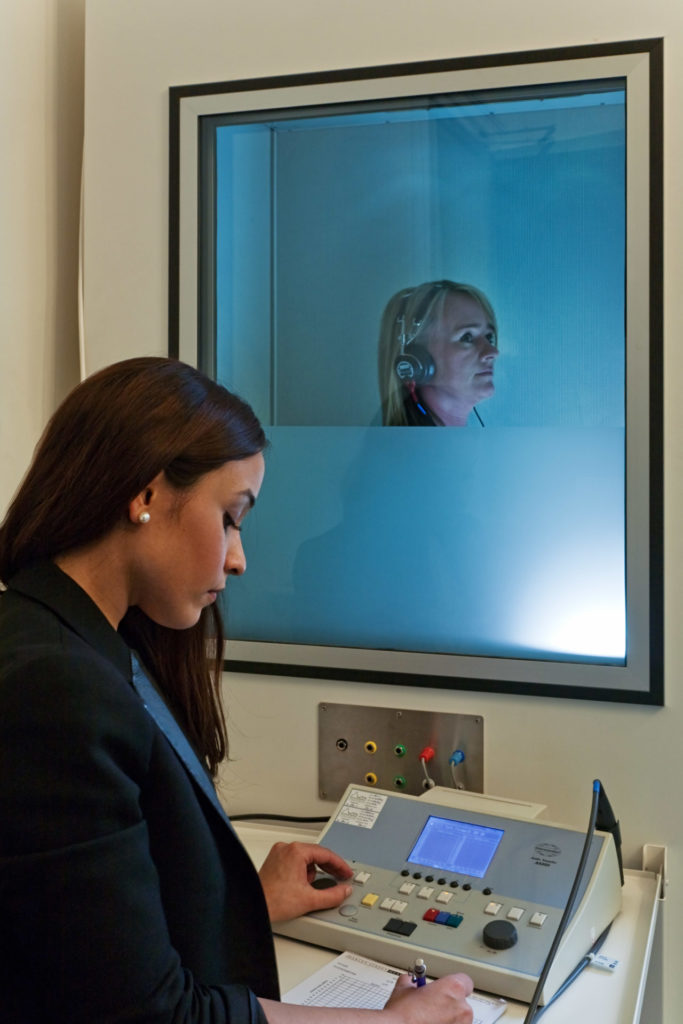

The hearing test process
The hearing test typically consists of several parts, each of which evaluates a different aspect of your ears to fully understand the whole hearing pathway
Physical examination of the ear
The first step of a hearing test involves an examination of the ear using an otoscope. This device allows your clinical audiologist to inspect the ear canal and eardrum for any abnormalities, such as earwax buildup, infections or damage to the eardrum.
If any issues are found, the audiologist may recommend additional testing or refer you to an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) consultant for further evaluation.
A pure tone audiometry test
Pure tone audiometry is a test that evaluates your ability to hear different frequencies and pitches of sound. During the test, you will be asked to wear headphones and listen to a series of tones at varying frequencies and volumes.
Your clinical audiologist will ask you to indicate when you hear the sound by pressing a button. This test allows your audiologist to determine the softest sounds that you can hear at each frequency tested.
![]()
Other types of hearing tests
These tests are not a part of a standard hearing test and are sometimes requested if you have been referred by an ENT consultant or physician.
Speech audiometry test
Speech audiometry is a test that evaluates your ability to hear and understand speech. In this test, you will be asked to repeat a series of words or sentences that are presented to you at different volumes and in different backgrounds, such as in the presence of noise.
This test allows your clinical audiologist to determine your ability to understand speech in different listening conditions.
A middle ear assessment
The middle ear assessment is a test that evaluates the function of the middle ear, including the eardrum and the three tiny bones (ossicles) that transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
This test is typically conducted using a tympanometer, which measures the eardrum’s movement in response to changes in air pressure. This test allows your clinical audiologist to detect any problems with the middle ear, such as fluid buildup or a perforated eardrum.
An otoacoustic emissions (OAE) test
Otoacoustic emissions testing is a non-intrusive test that evaluates the function of the hair cells in the inner ear. This test is performed using a small probe that is placed inside the ear canal and a series of sounds are played to the ear.
If the hair cells in the inner ear are functioning correctly, they will emit a sound in response to the sound stimulus. This allows your clinical audiologist to determine the integrity of the hair cells in the inner ear and detect any damage or dysfunction.
An auditory brainstem response (ABR) test
Auditory brainstem response testing evaluates the function of the auditory nerve and brainstem pathways that transmit sound information to the brain. For this test, electrodes are placed on the scalp and behind the ears, and a series of clicks or tones are presented to the ear.
The electrodes detect the electrical activity generated by the auditory nerve and brainstem in response to the sound stimulus. This test allows your clinical audiologist to determine if there are any issues with the auditory nerve or brainstem that could be affecting hearing function.
![]()
What happens after a hearing test?
After the hearing test is complete, your clinical audiologist will review the results and share them with you. If you opt for a more detailed hearing assessment, your results will be discussed with you and there will be the opportunity to discuss any recommendations or management options that may be necessary.
If the test indicates that you have hearing loss, your clinical audiologist can recommend hearing aids or other assistive devices to help improve your hearing function. Your clinical audiologist may also provide advice for effective communication strategies and lifestyle modifications that can help improve your quality of life with hearing loss.
How to book a hearing test
To book an appointment for a hearing test or hearing assessment, simply fill in the form below and a member of our staff will be in touch with you. There will be an initial telephone consultation to understand whether you would benefit from either a hearing test or hearing assessment, and then we’ll arrange an appointment for you with one of our audiologists. For any further information or advice, contact us here.
Enjoy this article? You might be interested in some of our others: