Hearing loss is a common problem that affects millions of people around the world. It can be caused by various factors, including ageing, exposure to loud noise, ear infections, genetics, and certain medications.
The good news is that hearing loss can sometimes be prevented by taking certain measures. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the causes of hearing loss and how to prevent it.
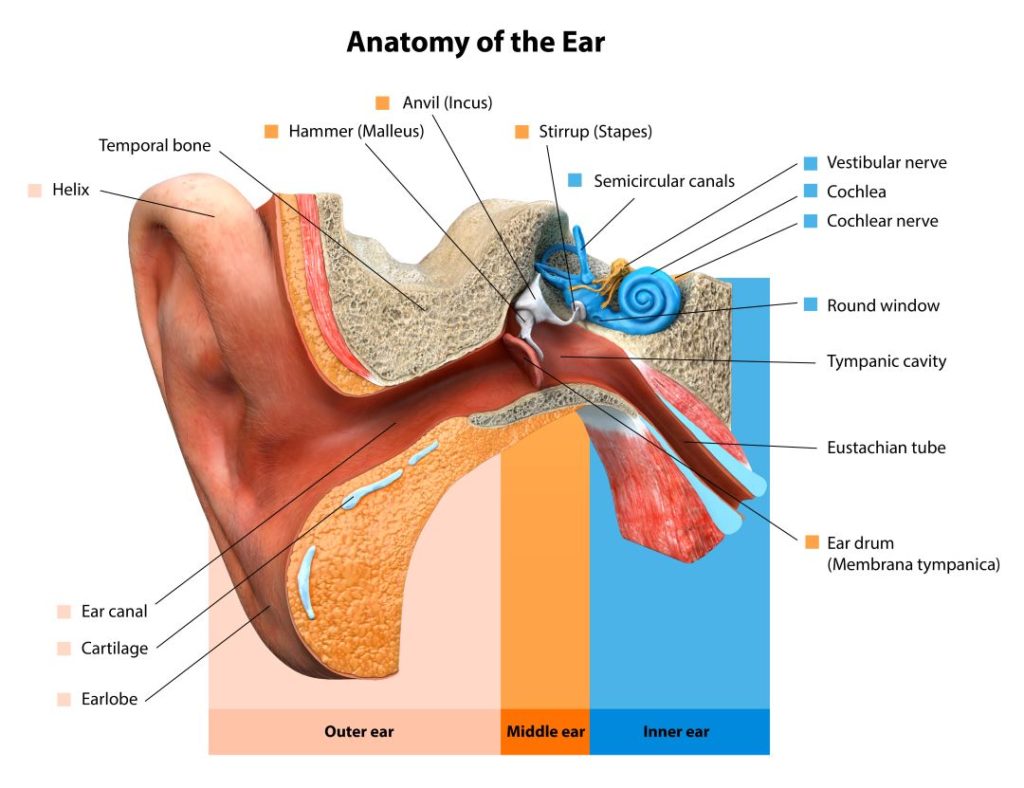
How hearing loss affects the ear
There is no single cause of hearing loss; it can come as a result of various factors that affect the outer, middle, or inner ear. Where your hearing loss occurs determines the type of hearing loss you’re experiencing, the severity and the best method of management.
Outer ear hearing loss
When the outer ear is damaged or blocked, sound waves cannot reach the eardrum effectively, resulting in hearing loss. This can be caused by earwax buildup, ear infection, or damage to the pinna or ear canal. In most cases, ear wax removal, surgery or hearing aids can help restore hearing loss caused by issues in the outer ear.
Middle ear hearing loss
The middle ear includes the eardrum and three small bones that amplify and transmit sound waves to the inner ear. When the middle ear is damaged or obstructed, sound waves cannot be transmitted effectively, leading to a loss of hearing.
This can be caused by an ear infection, fluid buildup or damage to the eardrum or bones. In some cases, medication or surgery may be needed to treat middle ear problems and restore hearing.
Inner ear hearing loss
The inner ear contains the cochlea, a spiral-shaped organ that converts sound waves into electrical signals that are then sent to the brain. When the hair cells in the cochlea are damaged or destroyed, the electrical signals cannot be transmitted effectively, resulting in hearing loss.
This can be caused by ageing, exposure to loud noise, certain medications and genetic characteristics. Hearing aids or cochlear implants are often recommended to help people with inner ear hearing loss.
What causes hearing loss?
One of the most common causes of hearing loss is ageing, which leads to a gradual decline in a person’s ability to hear, known as presbycusis. This type of hearing loss affects both ears equally and typically starts around the age of 60.
As we age, the hair cells in the inner ear that are responsible for detecting sound waves become damaged, leading to reduced sensitivity to high-frequency sounds.
If you’re hearing muffled sounds, a high-pitched ringing in the ear or are finding conversations challenging to keep up with when in noisy environments, you could be experiencing a loss of hearing capacity.
Book an appointment for a full diagnostic hearing assessment where our expert audiologist will test your hearing capacity and assist you in finding the right solution for better hearing.
Exposure to loud noise is another leading cause of hearing loss, particularly in occupational settings. Prolonged exposure to noise levels above 85 decibels can cause temporary or permanent hearing loss.
This can be caused by exposure to noise from machinery, power tools, or loud music, and can affect people of all ages. In addition to damaging the hair cells in the inner ear, exposure to loud noise can also damage the auditory nerve, which carries electrical signals from the ear to the brain.
The Control of Noise at Work Regulations 2005 aims to protect workers from excessive noise whilst at work and helps to protect against work-related hearing loss. This regulation requires employers to prevent risk and exposure to excessive noise and provide protective wear where necessary. We offer custom-made hearing protection earplugs to comfortably protect employees hearing whilst working in noisy environments.
Other causes of hearing loss include:
- Ear infections can cause temporary hearing loss if not treated promptly. Chronic ear infections can also lead to permanent hearing loss.
- Some types of hearing loss are caused by genetic factors which can be passed down from parents to their children.
- Certain medications, such as antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and some pain relievers, can cause hearing loss as a side effect, known as ototoxicity.
- Chronic illnesses such as diabetes can also lead to a loss of hearing capacity when managed poorly or left untreated.

How to prevent hearing loss
While some causes of hearing loss, such as ageing and genetic factors, are beyond our control, there are several steps we can take to prevent or reduce the risk of hearing loss.
Wear hearing protection when exposed to noise
One of the best ways to safeguard your hearing is to protect your ears from loud noise. This includes avoiding prolonged exposure to noise levels above 85 decibels, which can be harmful to your hearing.
When you’re exposed to loud noise, such as when attending a concert or working with noisy equipment, it’s important to wear custom earplugs or ear defenders to reduce the risk of long-lasting hearing damage.
Maintain good ear hygiene and care
Incorporating safe ear hygiene into your routine can also help prevent hearing loss. This means avoiding the use of cotton swabs or inserting other objects into your ears, which can damage the delicate skin and push earwax deep into the ear canal.
Instead, use a damp cloth or tissue to clean the outer ear and let the body naturally expel excess earwax. If your ears are uncomfortable and itchy, and you feel your hearing has decreased, this could be a sign that you need your ears professionally cleaned.
The safest and most effective way to clean your ears is to book an appointment for ear wax removal. We offer both ear irrigation and microsuction to remove wax buildup, alleviating discomfort and improving your hearing capacity.
Adopt a healthy lifestyle
Finally, adopting a healthy lifestyle can be a key factor in preventing hearing loss. This includes eating a balanced diet that is rich in vitamins and minerals that are important for hearing health, such as zinc, vitamin A, and magnesium.
Regular exercise is great for improving blood flow to the ears and reducing the risk of hearing loss. Additionally, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help protect your hearing and overall health. Managing chronic illnesses such as diabetes will also help prevent long-term hearing loss.
Book routine hearing assessments
A hugely important step in protecting your hearing and ear health is to book regular hearing screenings. Doing so will allow us to detect hearing loss early on and ensure you’re given prompt treatment and management.
If you are at risk of hearing loss due to age, noise exposure, or other factors, consider getting your hearing tested regularly by one of our expert audiologists. Routine checkups can help identify any hearing problems early on and allow for early intervention and treatment.
If you’re unsure if you need a hearing test, you can use our free online hearing test which takes as little as 5 minutes, all you need is a stable internet connection and headphones. This will give you an indication of your hearing but does not give an accurate hearing test. If it shows you may have a degree of hearing loss you should book in for a hearing test with an audiologist.
Enjoy this article? You might be interested in some of our others:










Recent Comments